The Evolution of 3D Printing Technology in the Healthcare Sector and Basic Concepts Technology in healthcare is advancing day by day, and these developments have the potential to fundamentally change treatment methods. 3D printing technology is at the center of this transformation, enabling faster, more effective, and personalized solutions to meet patients' needs. This technology, …
The Evolution of 3D Printing Technology in the Healthcare Sector and Basic Concepts
Technology in healthcare is advancing day by day, and these developments have the potential to fundamentally change treatment methods. 3D printing technology is at the center of this transformation, enabling faster, more effective, and personalized solutions to meet patients' needs. This technology, used in modern healthcare treatments, extends beyond prototype production to a wide range that includes the production of living tissues and organs through bioprinters.
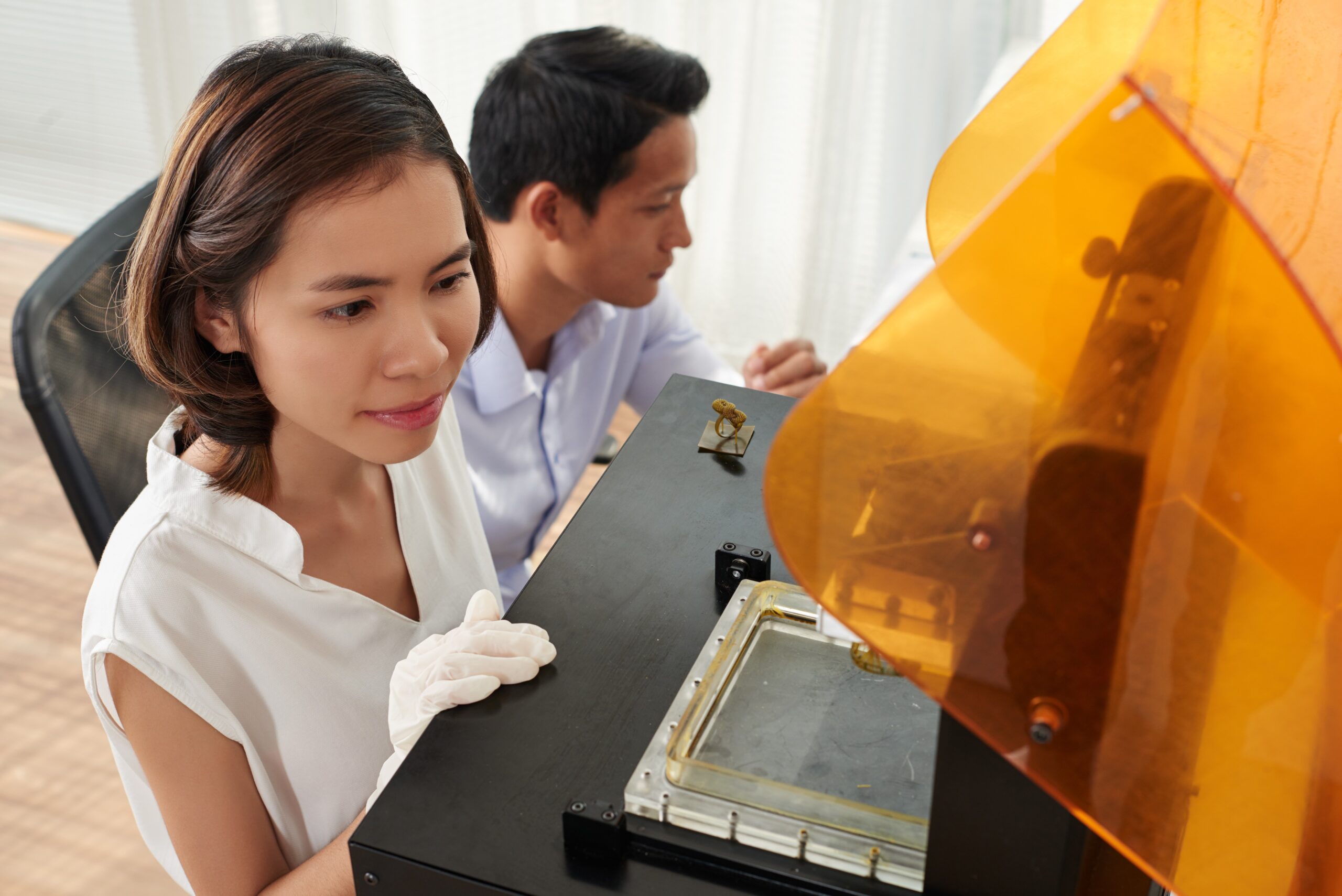

What is a 3D Printer? Basic Principles of 3D Printing in Healthcare
A 3D printer is a device that can create physical objects from digital designs. Medical 3D printers used in the healthcare sector produce complex structures layer by layer with high accuracy and speed. Compared to traditional manufacturing methods, this technology offers significant advantages in terms of both cost and time.
3D printing technology in healthcare is primarily used to create models tailored to patients' anatomy. For example, when designing a prosthesis or implant, the patient's exact measurements are modeled digitally, and products perfectly compatible with the individual are obtained through the 3D printer. This results in personalized solutions. Additionally, before surgical operations, doctors can view the patient's organ or problem details in three dimensions, allowing for more successful and safer surgeries.
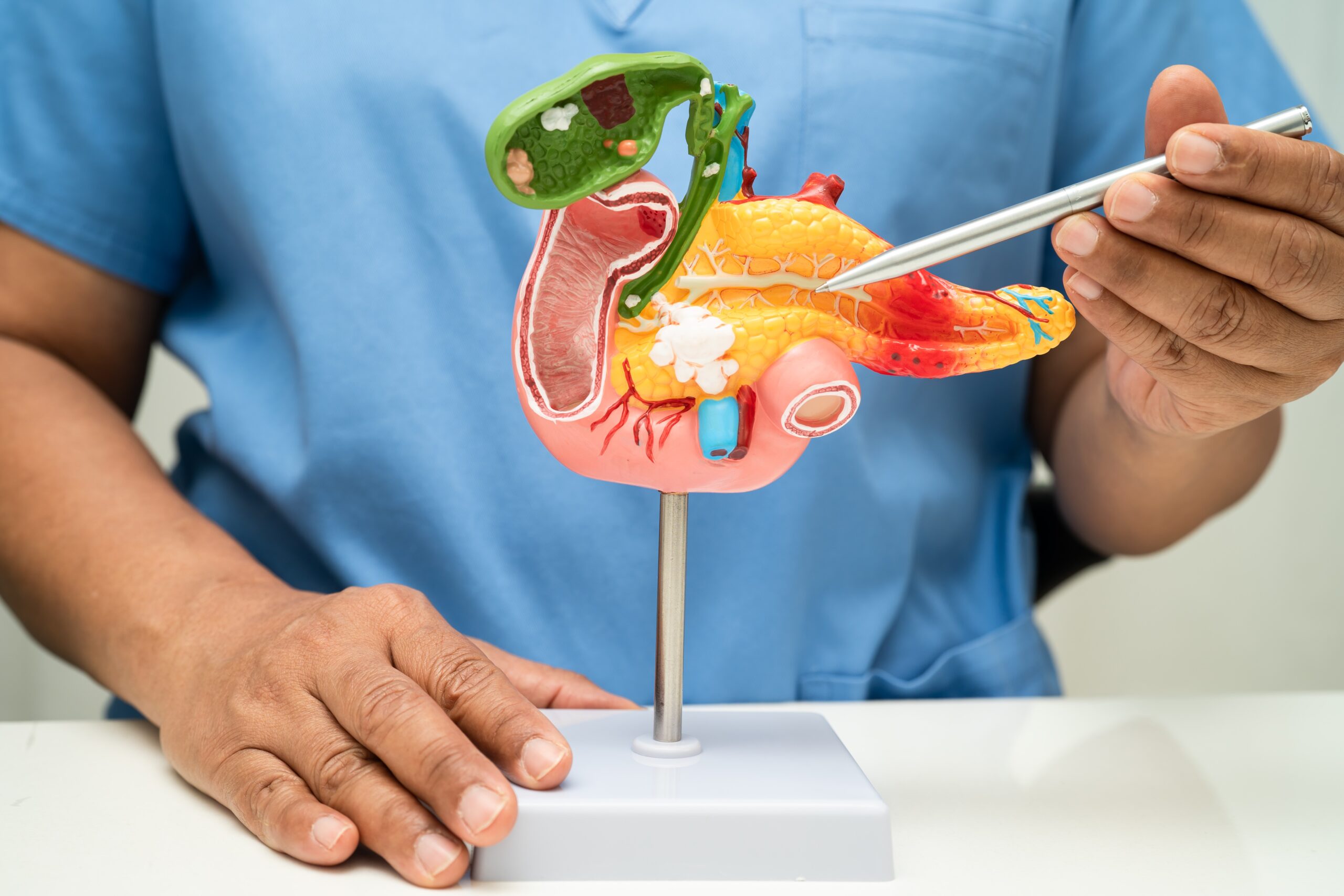
Use of 3D Printers in Modern Healthcare Treatments
The use of 3D printers in healthcare is not limited to the production of medical devices but is also widely adopted in medical research and education. For example, thanks to medical prototypes, new implants and devices can be tested and developed more quickly. This process accelerates the emergence of more effective and innovative treatment methods for patients.
Moreover, with bioprinter technology, it has become possible to produce tissues and organs in the laboratory by printing living cells layer by layer. This development offers hope for patients waiting for organ transplants and also forms the basis of personalized medicine applications. Producing tissues and organs suitable for each individual's genetic structure increases treatment success and minimizes side effects.
3D printing systems integrated with digital health technologies facilitate the spread of patient-centered treatments and improve the quality of healthcare services. Thus, patients receive treatments perfectly tailored to their needs rather than just standard solutions.
The Importance of 3D Printer Technology in the Healthcare Sector
Today, 3D printers have a wide range of applications, from the production of medical devices to surgical training models, from personalized prosthetics to organ engineering. The main advantages of this technology include speed, cost-effectiveness, and high precision. Additionally, it allows healthcare professionals to better plan and implement treatment processes.
3D printing technology in healthcare is not only a technical innovation but also a transformative tool that improves patient experience and increases the efficiency of healthcare services. Therefore, the use of medical 3D printers has become an indispensable part of modern medicine. The evolution of technology in the healthcare sector is accelerating thanks to the possibilities offered by 3D printing technology, enhancing the quality of life for more and more people every day.
The Role and Applications of 3D Printers in Personalized Treatments
One of the most important developments in modern medicine is the development of patient-specific treatment methods. Personalized medicine offers healthcare services tailored to patients' genetic structure, anatomical features, and lifestyles. In this approach, 3D printers stand out as one of the most important tools that make treatment processes more effective.
Production of Patient-Specific Prosthetics and Implants: Advantages and Examples
Every individual's body structure is different, and therefore standard prosthetics or implants may sometimes be insufficient. 3D prosthetics and medical implants produced using 3D printers enable the rapid and highly precise production of patient-specific products. As a result, prosthetics fit perfectly and the patient's comfort significantly increases.
Advantages include:
- Perfect fit and customization: Designed according to the patient's anatomical structure.
- Fast production: Prepared in a much shorter time compared to traditional methods.
- Cost-effectiveness: Offers economical solutions especially for the production of small and complex parts.
- Lightweight and durable materials: Increases patients' mobility.
For example, in orthopedic surgery, bone implants or prosthetic joints can be produced with 3D printing to perfectly match the patient's bone structure. This accelerates the healing process and reduces the risk of complications.
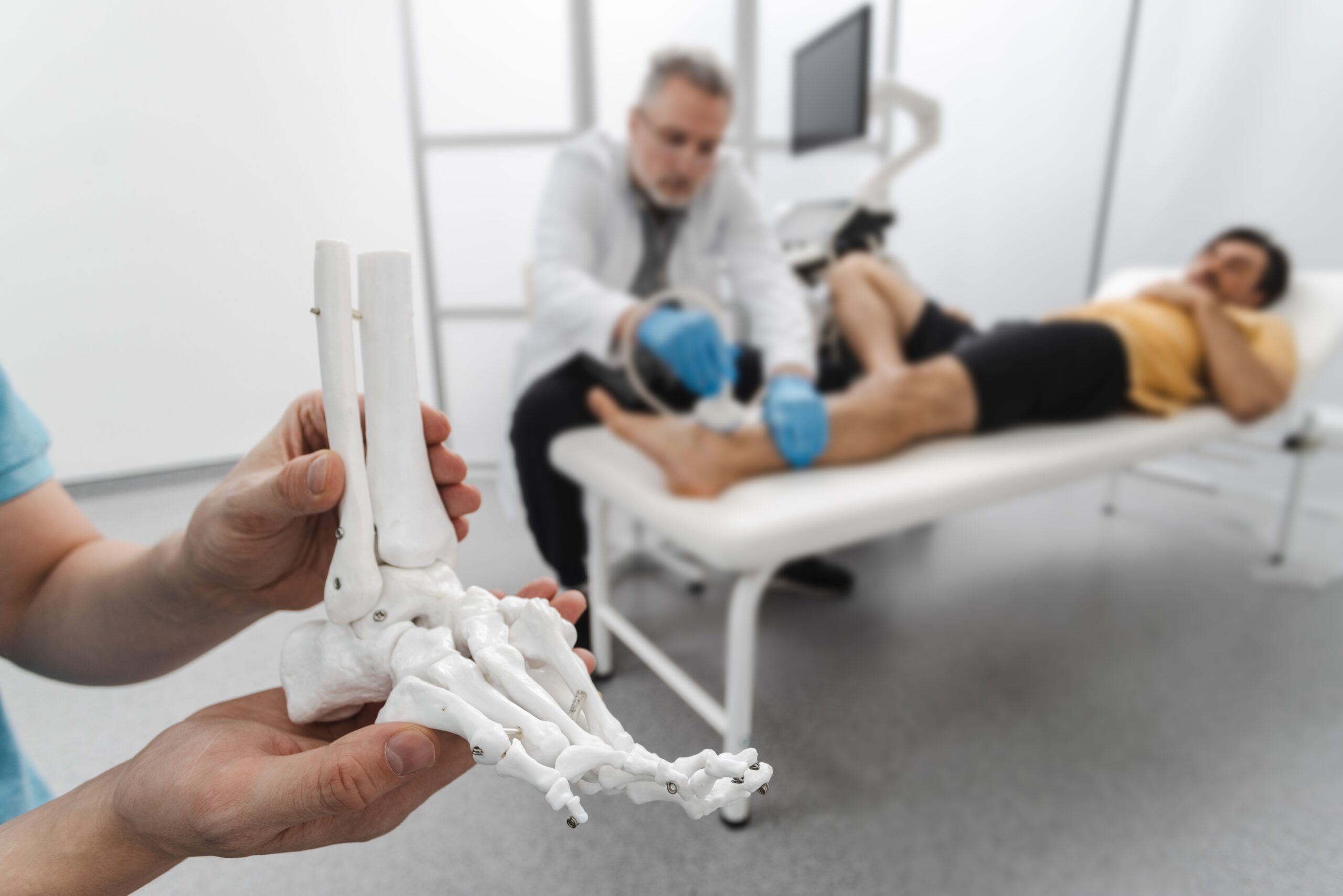
Use of 3D Models in Surgical Planning and Training
The success of surgical interventions depends on detailed planning and accurate execution. 3D printers produce life-sized models that help surgeons better understand complex anatomical structures. With these models, surgeons can simulate every stage of the operation before surgery, minimize risks, and shorten the duration of the procedure.
Additionally, these three-dimensional surgical models provide great benefits in medical education. Surgical trainees and healthcare professionals can practice on realistic models to improve their skills. This not only enhances patient safety but also contributes to the widespread adoption of new surgical techniques.
Organ and Tissue Engineering: Production of Living Tissue with Bioprinters
Bioprinter technology enables the production of artificial tissues and organs by printing living cells layer by layer. Advances in this field represent a revolutionary hope for patients waiting for organ transplants.
Within tissue engineering, organs produced with bioprinters using the patient’s own cells significantly reduce the risk of rejection by the immune system. Moreover, tissues produced in laboratory settings can be used in drug testing, allowing for the development of safer and more effective treatment methods.
This technology has the potential to offer personalized solutions for millions of patients awaiting organ transplants in the future. Thus, treatment processes will accelerate, and patient quality of life will improve significantly.
Contribution to Personalized Treatment
Personalized treatment methods developed through 3D printers form the foundation of patient-centered healthcare services. Products and models produced to meet the unique needs of each patient increase treatment success while minimizing side effects and complications. This is a critical factor that enhances patient satisfaction and treatment quality in the healthcare sector.
3D printer technology continues to revolutionize healthcare with personalized solutions and shapes the treatment methods of the future. The improvements it provides in patients' quality of life increase the importance of this technology in the healthcare field every day.
Innovative Health Treatments and Clinical Applications Developed with 3D Printers
3D printed health treatments offer innovative solutions beyond traditional methods, improving patients' quality of life. Technological advancements in this field are rapidly adopted, especially in critical health areas such as cancer treatment, dentistry, and regenerative medicine. 3D printers used in clinical applications make treatment processes more effective, precise, and customizable.
3D Print-Assisted Drug Delivery Systems in Cancer Treatment
Targeted and controlled release of drugs used in cancer treatment is an important approach that increases treatment efficacy and reduces side effects. 3D printing technology is a powerful tool for customizing and optimizing drug delivery systems. Thanks to this technology, drug carrier systems for cancer patients can be designed and produced according to the patient's needs.
Drug delivery systems developed with 3D printing ensure that the drug is released in a controlled manner within the body. Thus, toxic effects decrease, treatment duration shortens, and the patient's quality of life improves. Additionally, these delivery devices, designed with complex structures, enable drug doses to reach the exact targeted point.
This innovative approach marks an important milestone in cancer treatment technologies and is expected to be used more widely in the future.
Use of 3D Printing in Dentistry: Orthodontic Appliances and Crowns
Dentistry offers patients superior solutions both aesthetically and functionally thanks to 3D printed dentistry. Orthodontic appliances and dental crowns used in orthodontic treatments can be produced much faster and more precisely with 3D printers compared to traditional methods.
This technology allows for the preparation of products that perfectly fit the patients' oral structure. Thus, the treatment process shortens, patients experience more comfortable treatments, and treatment success increases. Additionally, the design process for dentists can be easily managed digitally and quickly revised when necessary.
Orthodontic appliances produced with 3D printing, as an important part of personalized treatment, increase patient satisfaction while offering cost-effective solutions. In crown and bridge production, restorations become more durable and aesthetic due to high precision.
3D Printing Applications in Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine is a field aimed at the renewal of damaged tissues and organs, and 3D printing applications for tissue regeneration are gaining increasing importance here. In these applications, which are among 3D printed health treatments, bioprinters are used to create cell-based structures in laboratory settings.
Thus, living tissue pieces compatible with damaged tissues can be transplanted to the patient. Regenerative medicine revolutionizes the treatment of chronic diseases and traumas while supporting the body's own healing mechanisms. 3D printing technology accelerates this process and enables more successful outcomes.
Clinical 3D printing applications have started to be used not only in laboratory environments but also in patient-centered treatments. These developments expand treatment options and positively affect patients' recovery processes.
Advantages Brought by 3D Printing in Innovative Health Treatments
- Patient-specific solutions: Every stage of the treatment is tailored to the patient's needs.
- Faster production: Saves time especially in emergency situations.
- High precision: Complex structures and small details can be easily produced.
- Cost-effectiveness: Offers economical solutions even for customized products.
- Increased treatment success: Treatment outcomes become more predictable and effective.
These advantages ensure the rapid spread of 3D printing technology in the health sector and its standardization in clinical applications.
Innovative health treatments developed with 3D printers not only offer more effective and personalized solutions to patients but also facilitate the work of health professionals and open new horizons in medicine. With the continuous development of this technology, much broader application areas will emerge in the near future.
Challenges Faced by 3D Printers in the Health Sector and Future Perspectives
While 3D printer technologies offer great opportunities in the health field, they also bring various challenges and obstacles. Overcoming these challenges is critical to ensuring widespread and safe use of the technology. At the same time, future developments will allow these barriers to be overcome and enable broader integration of 3D printing in the health sector.
Regulatory and Ethical Issues: Approval Processes and Patient Safety
Like every new technology used in healthcare, medical 3D printers must undergo strict regulatory body controls and approval processes. These processes are essential to ensure patient safety and minimize potential risks. However, the standardization and certification of medical devices and bioprinted products produced by 3D printing is a complex process.
Ethical rules are particularly significant discussion topics in the field of live tissue and organ production. Issues such as the use of cellular materials, patient consent, the safety of biological materials, and fair access must be addressed with ethical rigor. Medical technology regulations are continuously updated to ensure that these new applications are developed in a safe and ethically acceptable manner.
However, uncertainties in regulatory processes and differences in international standards can slow the widespread adoption of 3D printer use in the health sector. It is important that these regulations, which prioritize patient safety, are aligned with technological advancements.
Cost, Accessibility, and Technological Limitations
The use of 3D printers in healthcare may initially require high costs. Advanced technologies, such as bioprinters, demand investment both in devices and materials. This situation can particularly hinder accessibility in healthcare institutions with limited resources. Without achieving cost-effectiveness, the widespread adoption and integration of the technology into healthcare services may remain limited.
Technological limitations also pose a significant barrier. For example, the production of fully functional and complex organs with bioprinters is still in the research phase and has not been fully integrated into clinical applications. Challenges include keeping the produced tissues alive for extended periods, achieving functionality, and compatibility with the body.
Additionally, technical factors such as material diversity and durability in the 3D printing process directly affect treatment success. Therefore, quality control and reliability of products to be used in the health sector are critical issues.
Future Potential Developments of 3D Printers in Healthcare
Despite all challenges, the future of 3D printers in healthcare looks quite promising. With technological advancements, costs are expected to decrease and device accessibility to increase. This will open significant doors, especially in the fields of personalized medicine and regenerative medicine.
In the near future, the ability to produce more complex and functional organs in laboratory settings could offer revolutionary solutions for patients waiting for organ transplants. Additionally, further optimization of 3D-printed drug delivery systems and medical devices will enhance treatment success.
The acceleration of innovation in healthcare will also bring the integration of digital health solutions and artificial intelligence with 3D printers. This will make treatment processes more efficient and predictable, raising patient safety to the highest level.

With the spread of technological developments and innovations in the healthcare sector, the role of 3D printers will increasingly grow, and new treatment methods will emerge. These developments are critically important to meet the expectations of both healthcare professionals and patients.
Integration of 3D Printers in Modern Healthcare Treatments and Patient Benefits
The integration of 3D printers into the healthcare sector creates a transformation that directly positively affects the efficiency of clinical processes and patients' treatment experiences. This integration provides significant advantages for both healthcare professionals and patients.
Impact of 3D Printing Integration in Clinical Processes on Patient Outcomes
The use of 3D printing technology in clinical applications makes a difference at many stages, from treatment planning to implementation. 3D models used in surgical operations reduce the risks of the operation, shorten the surgery duration, and decrease complication rates.
Additionally, the production of medical implants and prosthetics tailored to the patient reduces problems caused by implant incompatibility. This accelerates the recovery process and increases treatment success. Thanks to clinical 3D printing applications, treatment protocols become more flexible and customizable.
As a result, patients' responses to treatment are positively affected, and their quality of life significantly improves. The integration of 3D printing in clinical processes increases the efficiency of healthcare systems, enabling the provision of quality services to more patients.
Advantages of Personalized Treatment and Improvements in Quality of Life
Personalized treatments maximize treatment effectiveness because they are designed according to patients' own physical and biological characteristics. 3D printers enable the rapid and precise production of these personalized products.
These advantages include:
- Better fit and comfort: Prosthetics and implants perfectly match the patient's anatomy.
- Reduced risk of complications: Problems caused by improper fit are minimized.
- Faster recovery: Treatment processes accelerate, and patients return to daily life in a shorter time.
Thus, patients recover more quickly, and the difficulties experienced during the treatment process decrease. These innovative solutions offered by 3D printer technology enhance the quality of modern healthcare services and make significant contributions to patients' quality of life.




